Understanding Hormonal Imbalance in Men in Milford, MA
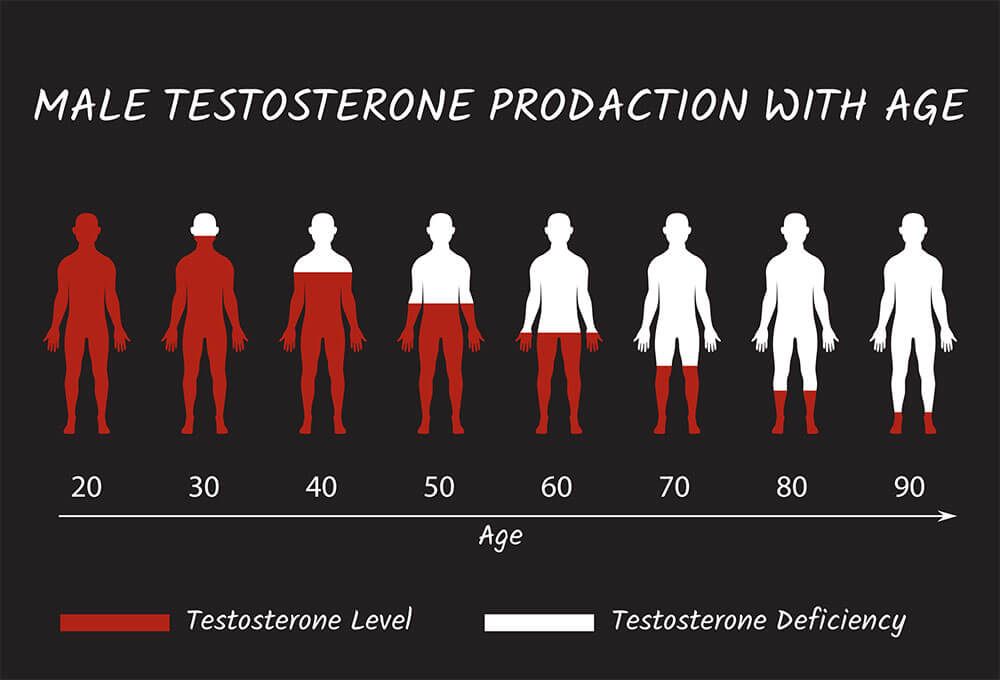
Low testosterone, also known as Low T or andropause, affects more than three million men in the U.S. and the prevalence increases with age. Research suggests that around age 45, nearly 40 percent of men will begin to experience symptoms of low testosterone. Testosterone levels begin to decline in a man around his late 20s and recede over time. By age 40, most men notice at least one or two symptoms of andropause or low testosterone. Many men will brush off these symptoms as side effects of aging and delay or never seek treatment.
If you have been experiencing a decrease in your sex drive, weight gain or loss of muscle mass, or perhaps a lack of energy and are easily fatigued, you may have Testosterone Deficiency (Low T).
The good news is that Low T can be effectively treated by a urologist. At Urology Specialists of Milford, men’s sexual health expert Dr. Steinberg specializes in diagnosing and treating Low Testosterone in men. Please contact our office to schedule a consultation.
What is Low Testosterone in Men?
Testosterone is the hormone responsible for a man’s sex drive. When a man is diagnosed with Low Testosterone, he may be experiencing erectile dysfunction, low libido, lack of energy, difficulty focusing, and other symptoms.
Low Testosterone (Low T), otherwise known as Hypogonadism, is a medical condition in which the body doesn’t produce enough testosterone — the hormone that plays a key role in maintaining a man’s energy level, sex drive (libido) and erection quality.
What Are the Causes of Low Testosterone in Men
Other Causes of Low Testosterone include:
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Chronic medical conditions (especially liver or kidney disease)
- Infections
- Hormonal disorders
- Medications (narcotics, chemotherapy)
How is Low Testosterone Diagnosed in Men?
Low testosterone is often an under-diagnosed condition in men because other psychological and medical conditions, as well as medications, can cause the same symptoms that are caused by Low Testosterone. Since Low Testosterone increases as men age, many men believe they must simply accept the way they feel as part of the natural aging process.
A simple blood test to check for a testosterone deficiency, often administered in the early morning, is typically the first way to diagnose the condition.
Dr. Steinberg orders the measurement of morning total and free testosterone blood levels which can help establish the diagnosis of hypogonadism. LH, FSH and Prolactin are specialized blood tests which are ordered to determine whether the issue arises from the testicle or from abnormal brain hormone levels. To further clarify the cause of hypogonadism, hormonal testing such as thyroid function tests and sex hormone binding globulin levels may be ordered.
While it is generally accepted that a testosterone level of less than 300 is considered low, low testosterone levels do not automatically warrant treatment. Dr. Steinberg believes a patient’s clinical symptoms are equally as important as Testosterone levels to decide if Testosterone Replacement Therapy is appropriate.
What Are the Signs of Low Testosterone in Men?
The most common signs of Testosterone Deficiency are a Decrease in Energy Level, Changes in Mood, Decreased Libido or Loss of Sex Drive, Erectile Dysfunction, Weight Gain or Hair Loss.
Other signs of Low Testosterone are Loss of Muscle Mass, Decreased Exercise Endurance, Brain Fog or Changes in Cognitive Focus, or Loss of Muscular Strength.
Learn More About the Symptoms of Low Testosterone Here.
Complications of Low Testosterone in Men
Ignoring the symptoms of Low Testosterone can not only impact Sexual Health and wellbeing, but also contribute to additional health issues and conditions. For example, continued loss of muscle mass and weight gain can be linked to medical conditions, such as high blood pressure and heart disease. Fatigue and low energy often result in a sedentary lifestyle that can lead to other health risks. The psychological and emotional difficulties often associated with Low Testosterone can also be detrimental to overall health and wellbeing.
What Should I Do if I Have Low Testosterone Signs?
If you suspect that you are experiencing signs of Low Testosterone, it is very important that you make an appointment with a urologist for an evaluation and consultation. As part of your consultation, a urologist will usually conduct blood tests to check your testosterone levels and determine the underlying cause of your Low T symptoms. Based on the results, your urologist will make a final diagnosis and may recommend Testosterone Replacement Therapy to help optimize testosterone levels and resolve symptoms.
Learn more about Testosterone Replacement Therapy Here.
There is no need to suffer with symptoms of Testosterone Deficiency. Dr. Steinberg is an expert in diagnosing and treating Testosterone Deficiency (Low T), and we want to help. To make an appointment for an evaluation with Dr. Steinberg in his Milford, MA office, please call Urology Specialists of Milford at (508) 473-6333.